Pelanor Cost Allocation Strategies
Cost Allocation Strategies Overview
Cost Allocation Strategies (CAS) in Pelanor let you distribute shared costs across the dimensions that matter to your business. Typical uses include:- Splitting recurring CSP costs (licensing, support fees) evenly across departments
- Allocating shared networking costs to product lines based on proportional usage
- Spreading data-warehouse costs to departments by query volume or runtime
Viewing and Editing Cost Allocation Strategies
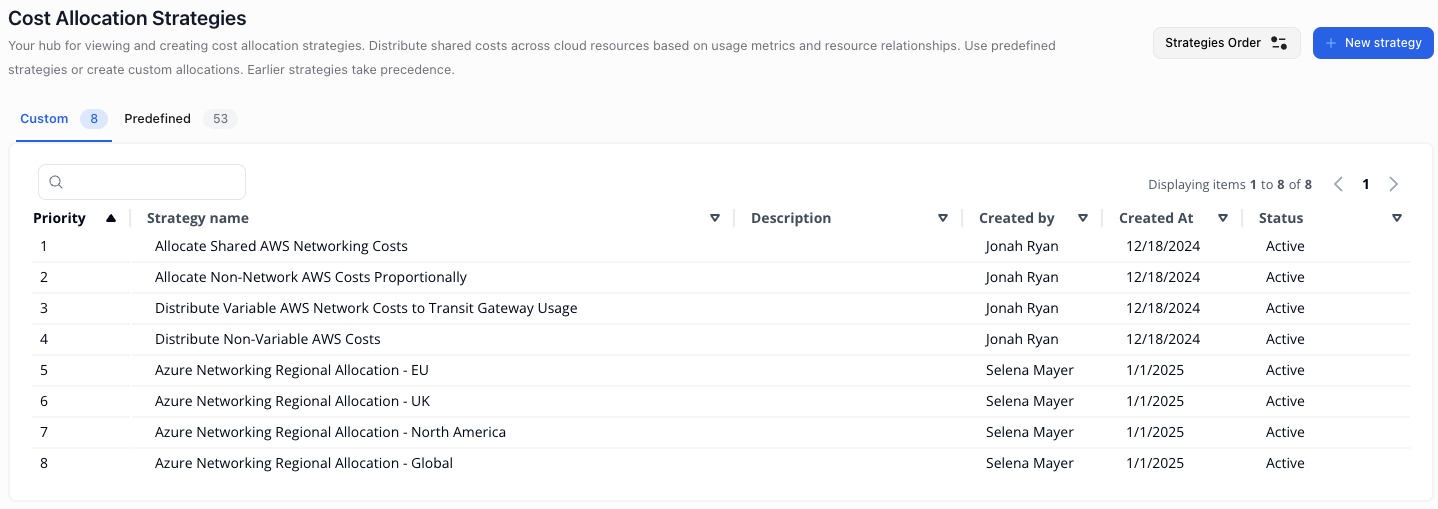
Open Settings → Cost Allocation Strategies to manage strategies.
Custom vs. Predefined Strategies
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Predefined | Maintained by Pelanor to handle nested entities (e.g., databases → VMs). Read-only. |
| Custom | Created by users with Admin / Workspace Admin roles. All others are read-only. |
Strategy Execution Order
Strategies run top-to-bottom. Re-order them using Strategies Order. Example:- Distribute Specific Network Costs by Usage – allocate VPC/ELB costs to departments
- Allocate Remaining Costs Equally – split licensing/support fees among departments
Allocation Types
Pelanor supports three types of cost allocation:Segment Allocation (most common)
Splits costs to custom dimension segments (e.g., departments, product lines). When to use:- You need a high-level breakdown by org units
- Simplicity is more important than fine-grained accuracy
| Setting | Notes |
|---|---|
| Allocation Method | Proportional, Fixed, or Metric-based |
| Dimension | Dimension whose segments receive the allocation |
Relational Allocation
Maps costs among interdependent resources (e.g., DB costs to workloads). When to use:- You need usage-based splits that follow cross-service relationships
- Filter (optional) – limits the source cost pool
Scope Allocation
Allocates costs by cloud scopes: Billing Account, Subaccount, Region, AZ. When to use:- You need visibility by infra/geography rather than business team
| Setting | Notes |
|---|---|
| Distribution Scope | Billing Account, Subaccount, AZ, Region |
| Allocation Metric | Determines how costs are proportioned |
| Filter (optional) | Restricts source costs |
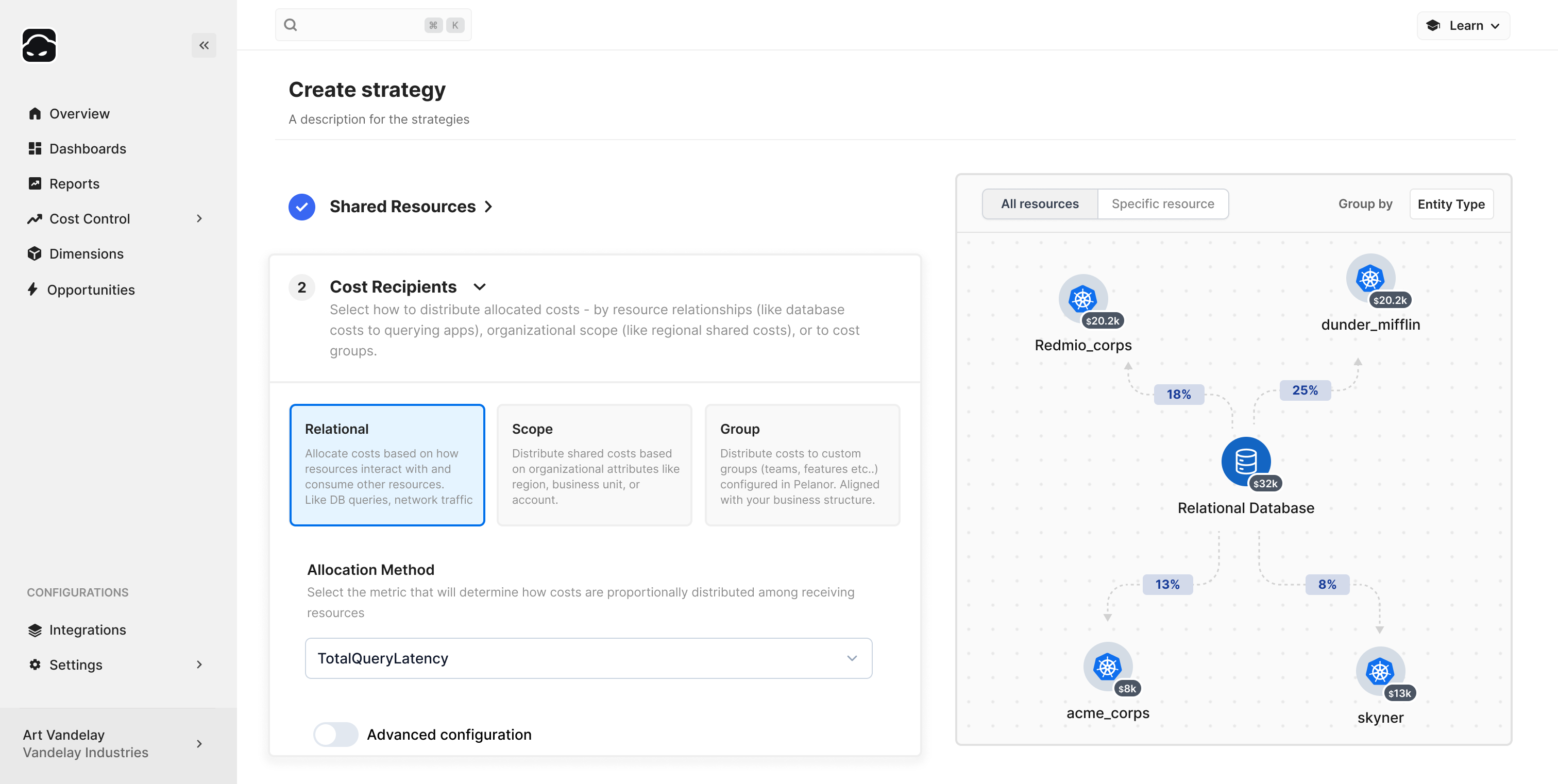
Creating a Cost Allocation Strategy
Define Source Costs
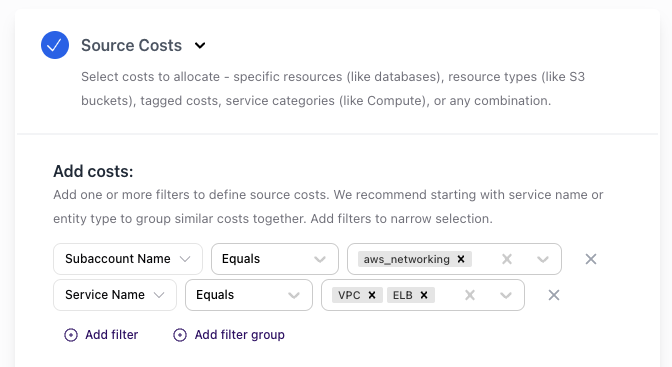
- Select allocation conditions – e.g., filter for
aws_networking,VPC,ELB - Configure waste allocation – default: Include Unutilized Capacity
- Choose usage subcategories – e.g., Cross AZ Traffic
- Core vs. Associated – use Associated unless it’s baseline (e.g., control plane)
Cost Recipient Configuration

See Allocation Types section above for detailed explanations.
- Select Allocation Type
- Choose Allocation Method
- Specify Parameters – dimension, metric, or fixed shares